CSIR or the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is the apex national Research and Development (R&D) organization of India. It is one of the world’s largest publicly funded Research and Development organizations. The CSIR HRDG -Human Resource Development Group offers various Grants, Research Fellowship schemes for individuals to pursue their research interests in various areas of Science & Technology.
This article is for all those individuals looking for detailed and updated information on CSIR NET, the admission process, eligibility, CSIR fellowships and more.
An Important Update: The National Testing Agency (NTA) has announced the re-opening of the online portal to submit an online application form or to complete the online application form for CSIR-UGC NET June 2020.
Topics covered
What is CSIR NET?
The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research National Eligibility Test or the CSIR NET is conducted to test the eligibility ‘for Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and for Lectureship/Assistant Professor’ in Indian universities and colleges. CSIR and University Grants Commission (UGC) provide Research Fellowships for training in methods of research under the guidance of faculty members or scientists working in University Department/ National Laboratories and Institutions in various fields of Science.
The online applications for CSIR NET are invited twice a year pan India through Press Notification of CSIR-UGC-NET for Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) and Lectureship/Assistant Professor (LS/AP).
The CSIR NTA conducts the examination for Junior Research Fellowship and Eligibility for Lectureship (LS)/ Assistant Professor for the following five subjects:
- Life Sciences
- Physical Sciences
- Chemical Sciences
- Earth, Atmospheric, Ocean and Planetary Sciences
- Mathematical Sciences
CSIR NET Exam
- CSIR-UGC (NET) Exam for Award of Junior Research Fellowship and Eligibility for Lectureship is a Single Paper Test with Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- The MCQ test will be of a total of 200 marks and will be conducted for each subject.
- The total duration of CSIR NET shall be of 3 hours.
- The question paper for each subject shall be divided in to three parts i.e. Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Take a look at the image below to under the CSIR NET Exam pattern:
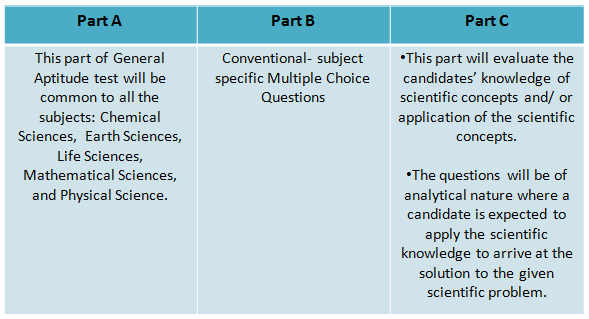
CSIR UGC NET Exam Pattern
As you have read an overview of the CSIR NET Exam above, let us now take a deeper dive into the CSIR Exam Pattern now and understand the exam pattern of all the five subjects we earlier talked about:
Chemical Sciences
| Category | Part A | Part B | Part C |
| Number of Questions | 20 questions | 40 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 60 |
| Questions to be attempted | 15 | 35 | 25 |
| The breakup of total marks per question (200) | 30 | 70 | 100 |
- The question paper is divided in three parts: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Part A consists of total 20 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 15 questions of two marks each.
- Part B consists of a total of 40 MCQ questions out of which candidates are to attempt 35 questions comprising of 2 marks each.
- Part C consists of a total of 60 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 25 of four marks each.
- Candidates must note that there will be negative marking @ 25% for each wrong answer.
Earth, Atmospheric, Ocean and Planetary Sciences
| Category | Part A | Part B | Part C |
| Number of Questions | 20 questions | 50 Multiple Choice Questions(MCQs) | 80 questions |
| Questions to be attempted | 15 | 35 | 25 |
| Breakup of total marks per question (200) | 30 (200) | 70 (200) | 100 (200) |
- The question paper is divided in three parts: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Part A consists of total 20 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 15 questions of two marks each.
- Part B consists of a total of 50 MCQ questions out of which candidates are to attempt 35 questions comprising of two marks each.
- Part C consists of a total of 80 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 25 of four marks each.
- Candidates must make note that for Part ‘A’ and ‘B’ there will be Negative marking @25% for each wrong answer. The Negative marking for Part ‘C’ will be @ 33% for each wrong answer.
Life Sciences
| Category | Part A | Part B | Part C |
| Number of Questions | 20 questions | 50 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 75 questions |
| Questions to be attempted | 15 | 35 | 25 |
| The breakup of total marks per question (200) | 30 (200) | 70 (200) | 100 (200) |
- The question paper is divided in three parts: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Part A consists of total 20 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 15 questions of two marks each.
- Part B consists of a total of 50 MCQ questions out of which candidates are to attempt 35 questions comprising of two marks each.
- Part C consists of a total of 75 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 25 of four marks each.
- Candidates must note that there will be negative marking of 25% for each wrong answer.
Mathematical Sciences
| Category | Part A | Part B | Part C |
| Number of Questions | 20 questions | 40 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 60 questions |
| Questions to be attempted | 15 | 25 | 20 |
| The breakup of total marks per question (200) | 30 (200) | 75 (200) | 95 (200) |
- The question paper is divided in three parts: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Part A consists of total 20 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 15 questions of two marks each.
- Part B consists of a total of 40 MCQ questions out of which candidates are to attempt 25 questions comprising of three marks each.
- Part C consists of a total of 60 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 20 of 4.75 marks each.
- Candidates must note that for Part ‘A’ and ‘B’ there will be Negative marking of 25% for each wrong answer and no negative marking for Part ‘C’.
Physical Sciences
| Category | Part A | Part B | Part C |
| Number of Questions | 20 questions | 25 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) | 30 questions |
| Questions to be attempted | 15 | 20 | 20 |
| The breakup of total marks per question (200) | 30 (200) | 70 (200) | 100 (200) |
- The question paper is divided in three parts: Part A, Part B, and Part C.
- Part A consists of total 20 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 15 questions of two marks each.
- Part B consists of a total of 25 MCQs questions out of which candidates are to attempt 20 questions comprising of 3.5 marks each.
- Part C consists of a total of 30 questions out of which candidates are to attempt 20 of 5 marks each.
- Candidates must note that will be negative marking of 25% for every wrong answer.
CSIR NET NTA: Overview of Programs & Fellowships
CSIR HRDG contributes significantly in the Research and Development in the areas of Science and Technology (S&T). To identify and determine the eligibility of talented individuals having the aptitude to work for the innovation and creation of advancement of knowledge and technology, CSIR HRDG indulges in various activities and fellowship programs.
To understand the various schemes and programs offered by the CSIR HRDG, the CSIR NET Eligibility section is divided in five sections:
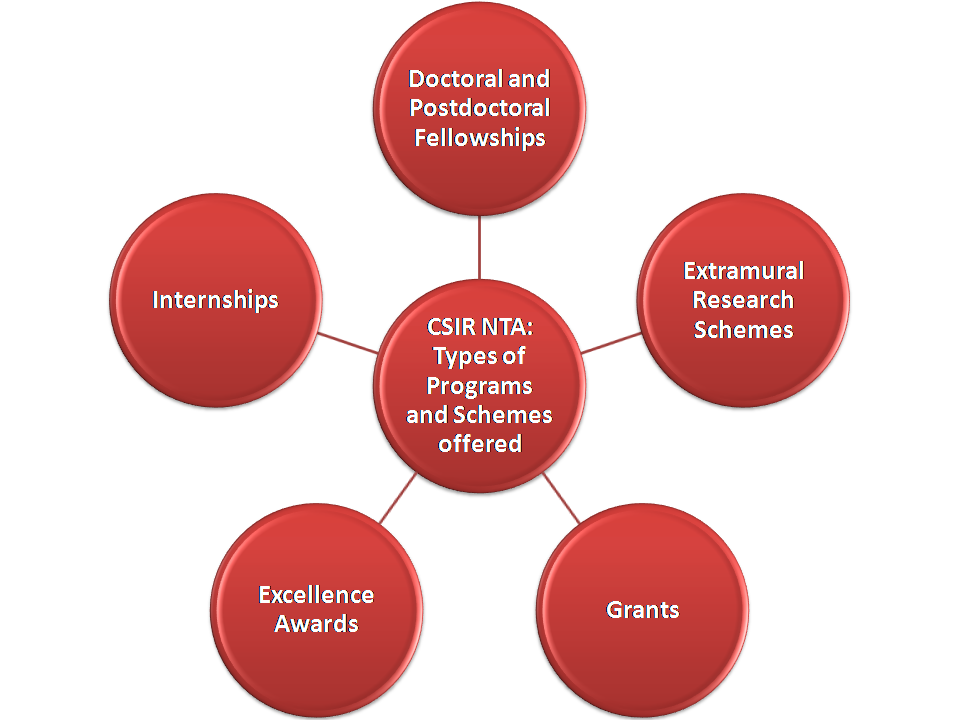
- Doctoral and Postdoctoral Fellowships
- Extramural Research* Schemes
- Grants for promoting knowledge sharing
- Promotion and Recognition of Excellence through Awards
- Internships
*Extramural, in an educational context, refers to the studies taken by a student away from the physical campus or a university but are provisional students of the university or institution. It can also be referred to as distance learning.
However, in this article, we will discuss only the Doctoral and Postdoctoral fellowships and understand the various fellowship schemes and programs offered by the CSIR NTA.
CSIR NET NTA: Eligibility, stipend & rewards + duration of program
Doctoral and Postdoctoral Fellowships
| Name of Program | Eligibility | Amount/ Stipend/ award | Tenure |
| Junior Research Fellowship (JRF- NET) | · Bachelors in Science (4 years)/ BE/ B. Tech/ B.Pharma/ MBBS/ Integrated BS-MS/ M.Sc. or Equivalent degree/ B.Sc. (Hons) or equivalent degree; or · Students enrolled in integrated MS-PhD program with at least 55%; or · Candidates enrolled for M.Sc. or having completed 10+2+3 years of the above qualifying examination are eligible for this program. Age Limit- 28 years | · Rs. 31000 per month with an annual contingency grant of Rs. 20,000. ·House rent allowance (HRA) according to the rules of the organization where placed, is admissible | 5 years, upgraded to SRF after 2 years |
| JRF-GATE | · BE/B. Tech degree holders in engineering discipline with valid GATE score; or · Candidates with B.Pharm. degree and having qualified GPAT. Age Limit- 28 years | Rs. 31000 per month with annual contingency grant of Rs. 20,000. | 5 years, upgraded to SRF after 2 years |
| Dr Shyama Prasad Mukherjee (SPMF) Fellowship | · Top 14 candidates each in Chemical and Life Sciences, and 7 candidates each in Earth, Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences in’ unreserved category will be taken from combined merit list of General/OBC/SC/ST/PWD. · The selected candidates will then be evaluated on the basis of interview. | Rs.36000/- + HRA per month during the first two years of the fellowship and a Contingency grant of Rs.70000/- p.a. | Initially for 2 years. Extendable as per normal rules for CSIR JRF (NET) scheme. Total of 5 years. Later upgraded as SRF. |
| Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) | ·M.Sc. / BE/ B.Tech. or equivalent degree with at least 55% marks and one publication in SCI Journal and should have completed at least two years of post M.Sc./BE/B.Tech. research experience; OR ·M.Tech/ ME or equivalent degree in engineering/ technology with at least 60% marks; OR ·BE/B.Tech. or equivalent degree with at least 60% marks and two years research experience as on the last date of application; OR ·MBBS/ BDS or equivalent with at least 60% marks and one year internship; OR ·B.Pharm/ BVSc/ B.Sc.(Ag) or equivalent degree with at least 55% marks and one publication in SCI Journal and should have completed at least three years research experience; OR ·MPharm/ MVSc/ MSc (Ag) or equivalent degree with at least 55% marks and one publication in SCI Journal and should have at least one year research experience. | ·The stipend for SRF has been discontinued. ·The fellowship grant money will be payable on a monthly basis to the candidates respective institution. ·An annual contingent grant of Rs.20,000/- per fellow is provided to the University/Institution. | 3 years; Total JRF + SRF tenure: 5 years |
| *Research Associateship (RA) | ·Ph.D. (in a science or engineering subject) or MD/MS/ MDS (in medical science subject) or ME/ MTech/ MPharm/ MVSc with three years R&D experience as on the last date of application, evidenced from RAship or associateship or from date of registration of PhD. ·The candidate applying for Research Associateship must have at least one research publication in standard refereed journal as listed in Journal Citation Reports (JCR). ·Candidates who have PhD (Science/ engineering) thesis submitted are also eligible for RA’ship. | ·Rs.47000/-pm or ·Rs. 49000/-pm or ·Rs. 54000/-pm with annual contingency grant of Rs. 20,000/- for all | 3 Years |
| Nehru Science Postdoctoral research Fellowship (PDF) | ·PhD degree holders within three years of award of the PhD degree; or ·Candidates who have submitted PhD thesis; or ·Applicants who are about to submit thesis are also eligible (admission will be conditional in such cases) | Rs. 65000 per month or with annual contingency grant of Rs. 3.0 Lakh | 2 years |
*Research Associateship- is offered to a certain number of Young research workers who have a potential in original research and propose to work in science, engineering, medicine or technology on specific projects.
CSIR-UGC NET Fellowships are acceptable in Universities/IITs/Post Graduate Colleges/ Government Research Establishments including those of the CSIR, Research & Development establishments of recognized public or private sector industrial firms and other recognized institutions. Take a look at some of the CSIR Laboratories down below:
List of 35+ CSIR Laboratories
- Advanced Materials and Processes Research Institute (AMPRI),Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- Central Building Research Institute (CBRI),Roorkee, Uttarakhand
- Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB), Hyderabad, Telangana
- Central Drug Research Institute (CDRI), Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- Central Electrochemical Research Institute (CECRI), Karaikudi, Tamil Nadu
- Central Electronics and Engineering Research Institute (CEERI), Pilani, Rajasthan
- Central Food and Technological Research Institute (CFTRI), Mysore, Karnataka
- Central Glass & Ceramics Research Institute (CGCRI), Kolkata, West Bengal
- Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (CIMAP), Uttar Pradesh
- Central Institute for Mining & Research (CIMFR), Jharkhand
- Central Leather Research Institute (CLRI), Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute (CMERI), Durgapur, West Bengal
- Central Road Research Institute (CRRI), Delhi
- Central Scientific Instruments Organization (CSIO), Chandigarh
- Central Salt and Marine Chemical Research Institute (CSMCRI), Gujarat
- Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (IGIB), Delhi
- Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (IICB), Kolkata, West Bengal
- Institute of Himalayan Bioresources Technology (IHBT), Himachal Pradesh
- Indian Institute of Chemical Technology (IICT), Hyderabad, Telangana
- Indian Institute of Integrative Medicine (IIIM), Jammu, J&K
- Indian Institute of Petroleum (IIP), Dehradun, Uttarakhand
- Indian Institute of Toxicological Research (IITR), Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- Institute of Minerals & Materials Technology (IMMT), Bhubaneswar, Orissa
- Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH), Chandigarh
- National Institute of Oceanography (NIO), Goa
- National Aerospace Laboratory (NAL), Bangalore, Karnataka
- National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI), Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
- National Chemical Laboratory (NCL), Pune, Maharashtra
- National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI), Nagpur, Maharashtra
- North-East Institute of Science and Technology (NEIST), Jorhat, Assam
- National Geographical Research Institute (NGRI), Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh
- National Institute of Interdisciplinary Science & Technology (NIIST), Thiruvanthapuram, Kerala
- National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources(NISCAIR), Delhi
- National Institute of Science and Technology Development Studies (NISTADS), Delhi
- National Metallurgical Laboratory (NML), Jamshedpur, Jharkhand
- National Physical Laboratory (NPL), Delhi
- Structural Engineering Research Centre (SERC), Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- CCSIR Fourth Paradigm Institute, Bangalore, Karnataka
CSIR NET Syllabus
Complete detailed syllabus for CSIR NET Exam for different subjects is given below:
CSIR NET 2020 Syllabus for Chemical Sciences
| Inorganic Chemistry | Physical Chemistry |
| Chemical periodicity | Basic principles of quantum mechanics |
| Structure and bonding in homo- and heteronuclear molecules | Approximate methods of quantum mechanics |
| Concepts of acids and bases | Atomic structure and spectroscopy |
| Main group elements and their compounds | Chemical bonding in diatomics |
| Transition elements and coordination compounds | Chemical applications of group theory |
| Inner transition elements | Molecular spectroscopy |
| Organometallic compounds | Chemical thermodynamics |
| Cages and metal clusters | Statistical thermodynamics |
| Analytical chemistry | Electrochemistry |
| Bioinorganic chemistry | Chemical kinetics |
| Characterization of inorganic compounds | Colloids and surfaces |
| Nuclear chemistry | Polymer chemistry |
| Organic Chemistry |
| IUPAC nomenclature of organic molecules |
| Principles of stereochemistry |
| Aromaticity |
| Organic reactive intermediates |
| Organic reaction mechanisms |
| Common named reactions and rearrangements |
| Organic transformations and reagents |
| Concepts in organic synthesis |
| Asymmetric synthesis |
| Pericyclic reactions |
| Synthesis and reactivity of common heterocyclic compounds |
| Chemistry of natural products |
| Structure determination of organic compounds |
| Other interdisciplinary topics to cover |
| Chemistry in nanoscience and technology |
| Catalysis and green chemistry |
| Medicinal chemistry |
| Supramolecular chemistry |
| Environmental chemistry |
CSIR NET 2020 Syllabus for Earth, Atmospheric, Ocean and Planetary Sciences
| Part A & B |
| The Earth and the Solar System |
| Earth Materials, Surface Features and Processes |
| Interior of the Earth, Deformation and Tectonics |
| Oceans and Atmosphere |
| Environmental Earth Sciences |
| Geology | Physical Geology |
| Mineralogy and Petrology | Geomorphology |
| Structural Geology and Geotectonics | Climatology |
| Paleontology and Its Applications | Bio-geography |
| Sedimentology and Stratigraphy | Environmental Geography |
| Marine Geology and Paleoceanography | Geography of India |
| Geochemistry | – |
| Economic Geology | Geophysics |
| Precambrian Geology and Crustal Evolution | Metereogoloy |
| Quaternary Geology | Ocean Sciences |
| Applied Geology (Engineering, Mineral Exploration, Hydrogeology) | – |
CSIR NET 2020 Syllabus for Physical Sciences
| Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology |
| Cellular Organization |
| Cell Communication and Cell Signaling |
| Fundamental Processes |
| Developmental Biology |
| System Physiology – Plant |
| System Physiology – Animal |
| Inheritance Biology |
| Diversity of Life Forms |
| Ecological Principles |
| Evolution and Behavior |
| Applied Biology |
| Methods in Biology |
CSIR NET 2020 Syllabus for Mathematical Sciences
| Unit-I & II | Unit-III |
| Analysis: Elementary set theory, finite, countable and uncountable sets, etc | Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) |
| Linear Algebra | Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) |
| Complex Analysis | Numerical Analysis |
| Algebra | Calculus of Variations |
| Topology | Linear Integral Equations |
| Descriptive statistics, exploratory data analysis | Classical Mechanics |
CSIR NET 2020 Syllabus for Physical Sciences
| PART – A (Core) | Part B (Advanced) |
| Mathematical Methods of Physics | Mathematical Methods of Physics |
| Classical Mechanics | Classical Mechanics |
| Quantum Mechanics | Quantum Mechanics |
| Electromagnetic Theory | Condensed Matter Physics |
| Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics | Nuclear and Particle Physics |
| Electronics and Experimental Methods | Atomic & Molecular Physics |
In Conclusion
In this article we discussed CSIR NET Exam, eligibility criteria, CSIR NET exam pattern and syllabus. As understanding the operations of an entire R&D organization is complex, getting into one is no doubt a huge feat. We hope you got some clarity about CSIR NET exam and are soon planning to sit for this exam.
Although preparing for CSIR NET Exam in itself means you are already sure what you are going to do, in case you wish to take second opinion from some expert counsellors, you may avail iDreamCareer’s professional services.
For detailed guidance, you can take help of our professional services which include:
Useful Links
- Tap to know more about the SHYAMA Prasad Mukherjee Fellowship.
- Learn more about the Senior Research Fellowships (SRF- Direct) fellowship stipend and other information.
- Find out about the programs and thrust areas of CSIR Laboratories
- Get more details about Junior Research Fellowships (JRF through CSIR-UGC NET)
- Know what is CSIR’S Junior Research Fellowship (JRF) – GATE
Some other topics you may find interesting:
- Top 50+ Scholarships for Indian Students: A Comprehensive Guide
- A Comprehensive Guide on Online Courses, Top 10 Free Online Courses, MOOCs, and much more
- MBA in Canada: An Ultimate Guide; Top 45 B Schools; Courses; Visa Application and more
- Complete Guide: Make a High Earning Career with an Automobile Engineering Degree
Shruti Verma has an experience of around 2+ years in research and analysis of careers, jobs, and industries. She has a knowledge of diverse fields spanning from career counselling, management consulting, engineering, and technology to science, finance, and humanities.












