Do you proudly wish to become a doctor too, like many of your mates? Are you looking for a guide on the MBBS courses in India? Are you aiming at an MBBS in India? Or have you already begun your preparations? Whichever it is, this post welcomes you to take a ride across. See you on the other side!
“Medicine is an artist whose magic and creative ability have long been recognized as residing in the interpersonal aspects of patient-physician relationship”
Hall, Roter & Rand, 1981
MBBS is in Latin and stands for Medicinae Baccalaureus Baccalaureus Chirurgiae (Surgery). However, we commonly refer to as “Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery”, which abbreviates to BMBS though!
Currently, NEET is the only exam in India that regulates admission to MBBS courses. NEET scores are also accepted for various other programs such as BDS, BHMS, BAMS, BUMS, BNYS, and BSMS, but tell me what your top choice is if you are considering appearing in NEET. It’s MBBS, right? Without further ado, let’s get started…
Topics covered
What all is covered in this post?
To make it easier for you, we have created a quick guide to everything you need to know about the MBBS course in India.

MBBS course details
MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) course is 5 and ½ years undergraduate degree with 4.5 years of course study and 1 year of mandatory rotational internship in various fields of medicine at hospitals, health centers, and health camps organized by non-profit organizations (NGOs).
To secure admission to an MBBS course in India, you must possess a minimum score of 50% or above in Class 12 in Physics, Chemistry & Biology with English mandatory.
Brief Description
The entire MBBS course is divided into 4 phases of around 50-56 weeks each and approx. 1400 teaching hours (according to the new curriculum by MCI) in which you will gain an overview of all the subjects including General Medicine, Respiratory Medicine, Paediatrics, Psychiatry, Dermatology, General Surgery, Ophthalmology, Gynaecology, Orthopaedics, etc. during the whole course. These 4 phases dovetails into a compulsory rotational internship of 1 – 1½ years.
Now, while you are in a certain phase, you can move to another subject in the same phase (horizontal integration) or another in a higher phase (vertical integration). This is subject to your performances in various formative assessments.
During the MBBS course, you will witness new teaching-learning methodologies including:
- Didactic Lectures
- Small group discussions
- Problem-based learning
- Case-based learning
- Demonstrations
- Direct observation, assisting and performing independently
- Formative Assessments
Dawn of a New Era Paradigm Shift – Major Change in UG Curricula for MBBS in India
The Government of India has introduced a new competency-based curriculum for MBBS from 2019 with a much higher focus on skills and competencies.
Dedicated time has been allotted for self-directed learning and co-curricular activities. Formative and internal assessments have been streamlined to achieve the objectives of the curriculum.
The intention of this change is to produce MBBS doctors who can recognize “health for all”, provide preventive, promotive, curative, palliative & holistic care to her patients as well as enable medical graduates to be prepared for the unknown (understand, investigate, treat & prevent new emerging diseases).

Competency-Based Medical Education (CBME): A new curriculum
The new curriculum clearly enunciates the competencies you, as an MBBS student, must be imparted and must learn, and clearly defines teaching-learning strategies and effective methods of assessment.
Besides, you will be trained to effectively communicate with patients and their relatives in a manner respectful of the patient’s preferences, values, beliefs, confidentiality, and privacy and for this purpose, an entire assessment framework as “Attitude, Ethics and Communication module (AETCOM)” has also been designed for MBBS students.
This is believed to be a change that is going to change the ‘shape’ and ‘face’ of undergraduate medical education in India to make it timely relevant, purposive, need-based, consequential, and impactful.
New MBBS curriculum in India
Below is the new MBBS curriculum in India as per Kumar S., Implementation of a new curriculum in UG (M.B.B.S): A dream project of medical education technology. Int.J.Med.Sci.Educ 2019;6(3):8-12:
| KEY ELEMENTS | FEATURES |
| CISP | The curriculum in GMR, 2019 is competency-driven CBME (Competency Based Medical Education) |
| Foundation Course | Explore and train the newly admitted to develop all type of skills, creative thinking, stress management and sensitize them for their future role of Indian Medical Graduate (IMG). |
| AETCOM Module | Mainly emphasizes Attitude, Ethics & Communication skill which is helpful to achieve IMG Goal. |
| ECE (Early Clinical Exposure) | Recognize the relevance of basic science in diagnosis, patient care, and treatment. It also improves understanding, interaction, and problem-solving skills. |
| PBL (Problem-Based Learning) | Problem based Learning enhances the knowledge in a specific area at the micro level |
| Integrated Teaching | Horizontal and vertical integration between and among disciplines. Basic and laboratory sciences (integrated with their clinical relevance) |
| Basic Research | Platform of all disciplines, working like a Consortium (Facilitation of Collaborative Research) |
| Self-Directed Learning | Interactive sessions, practical, clinical, group discussion, problem-oriented approach, case studies |
| Electives | Opportunities to students to acquire diverse learning experiences |
| Reflection and Metacognition | opportunity to reflect on their diagnostic approach, and think about what they could be missing |
MBBS Course Eligibility for NEET
Below is the eligibility of pursuing MBBS course in India:
- Your age shall mandatorily be between 17 (at the time of admission) to 25 years (as on the date of examination).
- Indian Nationals, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), Persons of Indian Origin (PIO), and Foreign Nationals are also eligible for admission through NEET subject to regulations as the case may be.
- You must have passed Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology/ Zoology/ Botany, and English individually and must have obtained a minimum of 50% marks taken together in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology/Biotechnology.
- If you have passed Class 12 from Open School or as a private candidate, you shall not be eligible to appear for NEET.
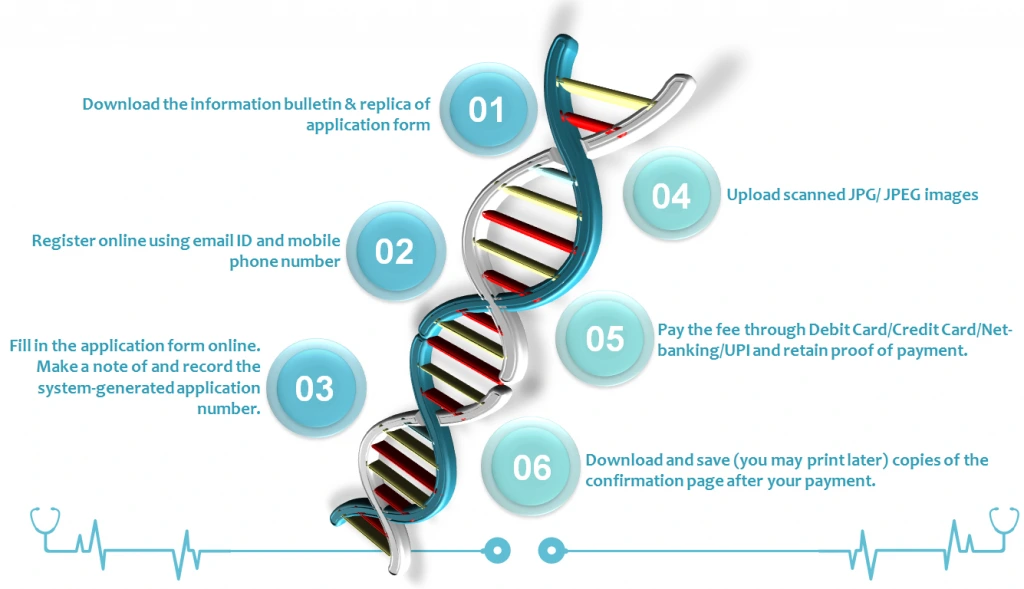
MBBS admission process in India
You need to clear NEET for admission. NEET is conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA).
- Registration for Entrance: you should register by logging in to the web portal, entering your personal details like your name, date of birth, mobile number, email ID, etc.
- Form Filling and Documents Upload: Once the registration is done, you have to fill the application form online by providing personal and academic details. Post successfully filling out the form, you will have to upload all the documents required.
- Payment of NEET Application Fee: you will have to pay the application fee after successfully filling out the form.
- Download Confirmation Page: After paying the application fees, if it shows ‘Confirmed’, take a printout of your application form & the confirmation page.
- Admit Card: admit cards will be issued to eligible candidates only.
- Entrance Exams: First, you need to appear for the exam and qualify with a good score.
- Counseling: Selected candidates will be invited for counseling sessions based on rank. If successful in NEET, you need to select the college of your choice from the colleges offered to you based on your rank. Once you have opted for your preferred college, you need to present the necessary documents authorities have asked for.
What to study after MBBS?
Today the competition is so steep that, after MBBS, getting yourself trained in some broad specialty is almost a necessity.
This (training in broad specialties) can be done in 2 ways: a Master’s degree or a Diploma.
After MBBS
- PG medical education in broad specialties is of 3 years duration in case of degree courses of MD(Medicinae Doctor)/ MS (Master of Surgery) after MBBS (MD is for physicians and MS is for aspiring surgeons).
- It is of 2 years in the case of a Diploma course after MBBS.
- Instead of MD/ MS (which you will pursue in government teaching hospitals), you may opt for “DNB” (Diplomate of National Board), which you will pursue in large private specialty hospitals.
- DNB and MD/MS are considered equivalent in terms of the academic worthiness of a candidate. However, you will find the majority going to government colleges instead of a private hospitals.
- You may also do a double Master’s like a DNB after MD/MS, to specialize in a particular area. For example, you may do MD in Internal Medicine and then go for DNB in Cardiology. There may be multiple other combinations depending on the area you want to specialize in.
After a Master’s degree in a broad specialty, to become a “super-specialized” doctor or a surgeon:
You have these options:
- DM and M Ch are degrees obtained after MD and MS respectively. DM is for doctors/ physicians and M Ch is for surgeons. The subjects at this level are called “super-specialties”. This is not possible if you have a Diploma after MBBS.
- However, one way to continue your education after Diploma can be if you do double post-graduation. Say suppose, you do a 2-year Diploma in Paediatrics and then a 3-year MD in Paediatrics followed by a higher degree of “DM” in Paediatric Cardiology. Now, this is only an example of a specific area of study. There can be many more combinations.
- If you have done DNB after MBBS, then your next option will be to complete super-specialty training through “FNB” (Fellow of National Board). FNB is considered equivalent to DM/M Ch.
Remember that by the time you complete a DM / MCh / FNB, you will have at least 8 years of practice experience, first as a junior resident (3 years during MD/MS / DNB), then as a senior resident (3 years during DM/MCh/ FNB) and considering 1-year gaps between MBBS and MD/MS / DNB and then another 1-year gap between MD/MS and DM/MCh/FNB.
Note: To have in-depth information on medical courses after 12th, refer to our Medical Courses in India after the 12th blog post!
Top 20 MBBS colleges in India
Here is the list of top 20 MBBS colleges in India as per NIRF ranking:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences
- Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research
- Christian Medical College
- National Institute of Mental Health & Neuro Sciences
- Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences
- Banaras Hindu University
- Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences & Research
- Jawaharlal Institute of Post Graduate Medical Education & Research
- Kasturba Medical College
- King George`s Medical University
- Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences
- Madras Medical College and Government General Hospital
- Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education And Research
- St. John’s Medical College
- Aligarh Muslim University
- Vardhman Mahavir Medical College & Safdarjung Hospital
- Maulana Azad Medical College
- Christian Medical College
- University College of Medical Sciences
- JSS Medical College
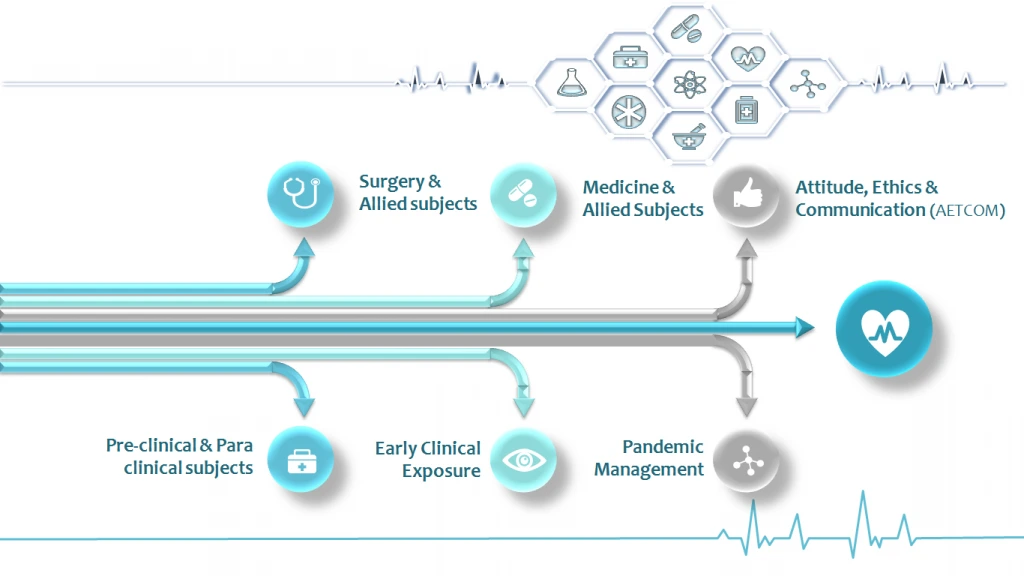
MBBS Course in India – Subjects
- Total course (5 & ½ year): 4 phases of around 50-56 weeks each and approx. 1400 teaching hours (according to the new curriculum by MCI) + compulsory rotational internship of1 – 1½ years.
- Now, while in a certain phase, you can move to another subject in the same phase (horizontal integration) or another in a higher phase (vertical integration).
- Integration (movement across phases) is subject to your performances in various formative assessments.
The 5 & ½ year new CBME MBBS curriculum is extensive, consisting of:
- Foundation course
- Orientation
- Medical profession & physician’s role
- Healthcare system
- National health priorities
- Allied health sciences
- Principles of family practice
- Alternate healthcare systems
- Skills Module
- Field Visit
- Professional Development including ethics
- Language, Computer Skills
- Sports & Extracurricular
- Orientation
- Pre-clinical and Paraclinical subjects:
- Human Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Pharmacology
- Pathology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine & Toxicology
- Medicine and Allied subjects
- Community Medicine
- General Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Psychiatry
- Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy
- Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
- Surgery and Allied subjects
- General Surgery
- Ophthalmology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Obstetrics &Gynaecology
- Orthopaedics
- Anesthesiology
- Radiodiagnosis
- Radiotherapy
- Dentistry
- Early Clinical Exposure (ECE)
- Attitude, Ethics, and Communication module (AETCOM)
- Alignment and Integration Module
- Skill Training Module
- Electives Module
- Pandemic Management Module
MBBS Course Fees
MBBS course fees vary depending on government and private colleges, with average MBBS course fees ranging from INR 10,000 to INR 6 Lakhs. A few examples are given in the table below. These are top MBBS colleges in India.
| COLLEGE | LOCATION | AVG ANNUAL FEES |
| AIIMS | New Delhi | Rs 1,628 |
| JIPMER | Puducherry | Rs 5,000 |
| Institute of Medical Sciences (Banaras Hindu University) | Varanasi | Rs 10,400 |
| Armed Forces Medical College | Pune | Rs 31,900 |
| Christian Medical College | Vellore | Rs 48,530 |
| King George’s Medical University | Lucknow | Rs 55,000 |
| Grant Government Medical College & Sir J J Group Of Hospital | Mumbai | Rs 60,000 |
| Seth GS Medical College & KEM Hospital | Mumbai | Rs 91,650 |
| St. John’s Medical College | Bangalore | Rs 5.5 Lakhs |
| Kasturba Medical College | Manipal | Rs 14.4 Lakhs |
Job and future prospects after MBBS course in India
Now, most lucrative prospects are concentrated for students with specialty training in any field of medicine. Most hospital doctors aspire to become a consultant. Consultants are specialized in their respective specialties.
MBBS doctors are not really worth a piece of cake in the competitive environment today. Anyhow, you will definitely have options of continuing independent practice right after MBBS and your licentiate exam (primary healthcare).
While you are interning, work shadowing or observing doctors is very helpful to get an idea of what your future work will involve.
The average entry-level salary of an MBBS graduate is between Rs 20,000-35,000. However, it can range up to Rs 8-10 Lakhs (for postgraduates only) depending upon your training experience and knowledge.
As an MBBS degree holder, you may start your career as a General Physician/ Junior Consultant Physician/ General Practice Doctor/ Primary Care Physician in various enterprises like:
- Government hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Private hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Residential nursing homes
- The military forces (possible only if you graduate from AFMC, one of the most prestigious colleges in India)
- Overseas aid agencies
- Voluntary & charitable organizations
- Research institutes
- Clinical trial organizations
- Pharmaceutical companies
There are also multiple opportunities to progress into academic or medical research within your specialist area but further qualifications will be required.
It’s a wrap!
After all of that mind-bender, you must be full of facts now!
You came looking for information about the MBBS course, MBBS subjects, MBBS course eligibility, and the MBBS admission process. We’ve served you a heck of much!
The undergraduate MBBS program is the foundation of the health delivery system in India. India has the distinction of having the largest number of medical schools as well as a large pool of health educators and numerous young Indian medical graduates joining the undergraduate medical education program.
It is a prestigious affair, being part of the healthcare fraternity as a care provider (doctor). You are entrusted with a Godly duty! The race of securing a seat in one of the many MBBS schools in India is long and tedious.
Are you sure your best bet is becoming a care provider?
Understanding the intricacies of any career is not child’s play. It requires an experiential assessment of your competencies (skills, abilities, knowledge & a lot more). So, career planning is an indispensable tool in your life and we can certainly help you with that. Plan now!
You can also get your queries resolved in just 60 seconds from our Career counselors. So, what are you waiting for? Download the app now!
iDreamCareer has helped millions of young minds like you from 9th class, 10th class, class 11, and class 12 discover their true mettle and is ready to help you too.
Must check these
- List of Colleges Teaching MBBS – MCI, India (total colleges 542 and total seats 80055)
- Search Colleges & Courses – MCI, India
- Black list doctors (Indian Medical Register) – MCI, India
- Competency Based MBBS Curriculum – MCI, India
- Pandemic Management Module – UG Curricula, MCI India
- Medical Counseling Committee (MCC)– After NEET
- Online counseling process – check for more details on counseling
- A dream project of medical education technology – A primary research study
Additional Info-Packed Links
- How to become a doctor in India?
- Ultimate guide to NEET
- NEET exam
- About NTA and changes in NEET
- MBBS in USA-Canada
- MBBS in Europe, Germany, UK
- Top scholarships to study abroad
- Careers that help to fight pandemics like CORONA
- Career in Optometry
- Medical courses without NEET
- Career in Radiology
- Study abroad: all you need to know

Anushree Rastogi is a Senior Content Writer at iDreamCareer, bringing over 5 years of expertise to the field of career counseling. She has done a PGDM in Marketing and Finance and possesses a unique blend of skills that allows her to craft engaging and informative content. She is passionate about helping individuals navigate their career paths and has dedicated her career to providing valuable insights through her content. Her commitment to excellence and keen understanding of the career landscape make her a trusted guide for those seeking professional direction. With a flair for clear and engaging writing, Anushree is on a mission to empower others to make informed and fulfilling career choices.


















